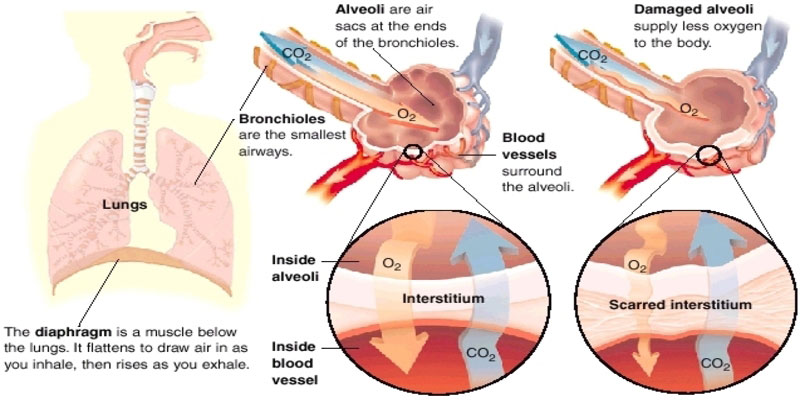
Several different lung diseases fall under the umbrella term "interstitial lung disease" (ILD), all of which hurt the interstitium, or the network of tissues and gaps that helps to hold the alveoli in place. In ILD, the interstitium, the tissue between cells, becomes inflamed or scarred, preventing the regular exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the body's tissues and resulting in respiratory distress and low blood oxygen levels. Environmental and occupational exposures, infections, medicines, and autoimmune disorders are only some of the many possible causes of ILD, making this a complicated and varied collection of conditions. The causes of ILD are sometimes puzzling (idiopathic).
Shortness of breath, persistent coughing, extreme exhaustion, chest pain, and loss of appetite are some symptoms that ILD can bring on. The severity of these symptoms may drastically impact the patient's quality of life. ILD's symptoms and radiographic findings can be similar to those of other lung disorders, making diagnosis difficult. An in-depth patient history, physical examination, and battery of diagnostic tests are essential for a precise diagnosis. Although ILD cannot be cured, it can be managed, and the quality of life for those who suffer from it can be enhanced via treatment. Medications, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lung transplants are all viable alternatives for treatment.
Inflammatory interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a class of lung diseases characterized by inflammation of the lung's interstitium. The symptoms can significantly affect the patient's quality of life, and the condition can be challenging to diagnose and treat. More study is required to learn more about ILD and its potential treatments.
Interstitial Lung Disease: What Causes It?
The underlying factors that bring on ILD range widely between the various forms of the disease. While environmental and occupational exposures, infections, medicines, and autoimmune illnesses have all been linked to autoimmune thyroiditis, the reason, in some cases, remains a mystery (idiopathic).
Subjection To Hazardous Conditions In The Workplace
ILD can be brought on by exposure to harmful substances at home or work. Dirt, mold, smoke, and chemicals are all contaminants. Farmers, construction workers, and miners are just some employees who face a higher risk of getting ILD owing to their jobs.
Infections
An infection may also bring on ILD. Pneumonia, TB, and fungal infections are among common examples.
Medications
ILD is a possible adverse effect of chemotherapeutic treatments and some antibiotics.
Chronic Inflammatory And Autoimmune Diseases

ILD is a potential complication of autoimmune diseases, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Indicators Of Interstitial Lung Disease
Depending on the subtype of ILD, symptoms might include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Have difficulty breathing, particularly when exercising
- persistent coughing
- Fatigue
- Pain in the chest
- Appetite loss
- Loss of Appearance
- Finger and toe clubbing (enlarged and rounded fingertips)
- Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis
ILD's symptoms and radiographic findings can be similar to those of other lung disorders, making diagnosis difficult. An in-depth patient history, physical examination, and battery of diagnostic tests are essential for a precise diagnosis.
Examination And Medical History
During the physical examination, the healthcare professional will inquire about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and any potential exposures to the environment or the patient's line of work. The patient's respiration and lung sounds will also be evaluated during the physical examination.
Exams And Checkups For Diagnosis
The following tests may be used to diagnose ILD:
- Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are used to evaluate lung health.
- Evaluation of lung tissue by high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest
- Methods involving bronchoscopy for the collection of lung tissue samples
- Diagnostic blood work for autoimmune diseases, infections, etc.
- Analyzing oxygen saturation values in arterial blood
What Can Be Done About Interstitial Lung Disease
The diagnosis and severity of ILD dictate the course of treatment. Although ILD cannot be cured, it can be managed, and the quality of life for those who suffer from it can be enhanced via treatment.
Medications

Possible medications for treating ILD are:
- Anti-inflammatory corticosteroids for the lungs.
- Immunosuppressants are drugs that dampen the immune system and thereby reduce inflammation.
- Lung fibrosis (scar tissue) can be treated with antifibrotic medicines.
Oxygen Treatment
To breathe, some persons with ILD may require oxygen therapy. Oxygen treatment has been shown to increase oxygen saturation and alleviate fatigue and difficulty breathing.
Rehab For The Lungs (Pulmonary)
As a form of treatment, pulmonary rehabilitation uses exercise and education to boost lung capacity, alleviate symptoms, and enhance the overall quality of life.
Transplantation Of New Lungs
Severe ILD patients may be candidates for a lung transplant. Those with terminal lung disease have a better chance of survival and improved quality of life after receiving a lung transplant.
Conclusion
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a collection of lung conditions that can seriously affect affected individuals. Environmental and occupational factors, infections, medicines, and autoimmune disorders can contribute to developing ILD. Proper testing and evaluation are crucial for effectively treating ILD, which can be challenging to diagnose. While there is currently no way to stop the progression of ILD, treatments can help with symptoms. Treatments, including oxygen therapy, medicine, and pulmonary rehabilitation, can reduce symptoms and restore lung function. Lung transplantation may be required in extreme circumstances.



